
Your router serves as the first line of defense against cyber threats, protecting your local network from dangers coming from the internet or even from infected devices already connected to your network. Just like the operating system on your computer or the apps on your phone, it is necessary to update the router's firmware periodically. This maintenance is crucial for fixing security flaws, maintaining optimal connection quality, and unlocking new features.
In this article, we'll review the risks associated with an obsolete router and walk you through the steps to update your router's firmware quickly and easily, ensuring your network remains secure and stable.
1. The Role of Firmware in Your Network’s Security
Firmware is essentially the router's brain—the core software responsible for managing network traffic, controlling all connected devices, and implementing the security protocols that defend your data. If the router is the gatekeeper of your local network, the firmware is the training that allows it to maintain security and order.
To keep your network alert and up-to-date against the latest cyber tricks, updating the router’s firmware to the newest available version is non-negotiable. As time passes without an update, your network gradually becomes both less efficient and far more vulnerable to security risks.
2. Risks of Obsolete Firmware
Updating your router's firmware as soon as the manufacturer releases new versions should be a routine part of maintaining a secure and stable internet connection. Neglecting this simple task exposes your network to several major risks:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Router manufacturers and security experts are constantly finding and patching security flaws. By not updating, cybercriminals can exploit known, uncorrected flaws to easily access your local network. This allows them to steal sensitive data, control your devices remotely, carry out attacks on other websites from your IP address, or enlist your device into a botnet.
- Poor Connection Performance: Firmware is key to optimizing network usage, ensuring all devices receive a stable, high-speed connection. Outdated firmware can lead to connection interruptions and browsing speeds slower than what you are paying for. Furthermore, updates often include performance improvements and new features, such as Wi-Fi time controls or built-in VPN service access.
- Incompatibility with New Devices: Security and connectivity protocols evolve rapidly. It is essential to update your router’s firmware to ensure it remains compatible with the most modern devices. Failure to do so might mean your new laptop or smart home device won't connect properly because the router doesn't recognize or support the required protocols.
To minimize these risks, you must periodically check for new updates and install them promptly. This is especially essential for modern routers, which receive frequent bug fixes and feature additions. For older routers, ensure you have the latest (even if dated) version installed, as it will be the most stable version ever released for that model.
3. How to Update Your Router’s Firmware in 4 Steps
While the exact procedure varies by router model and manufacturer, the process is generally straightforward. Older devices may require a completely manual process, while modern routers often include an option to automate updates during hours of inactivity.
Step 1: Access the Router and Check Status
Open a web browser on a computer connected to your network (via Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and access the router as an administrator using its IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) and your login credentials.
Once inside the configuration menu, look for the Firmware/Software Update section. Depending on the model, it may display the installed firmware version, indicate the availability of a newer version, or already have the update downloaded and ready for installation.
Step 2: Obtain the Latest Firmware File
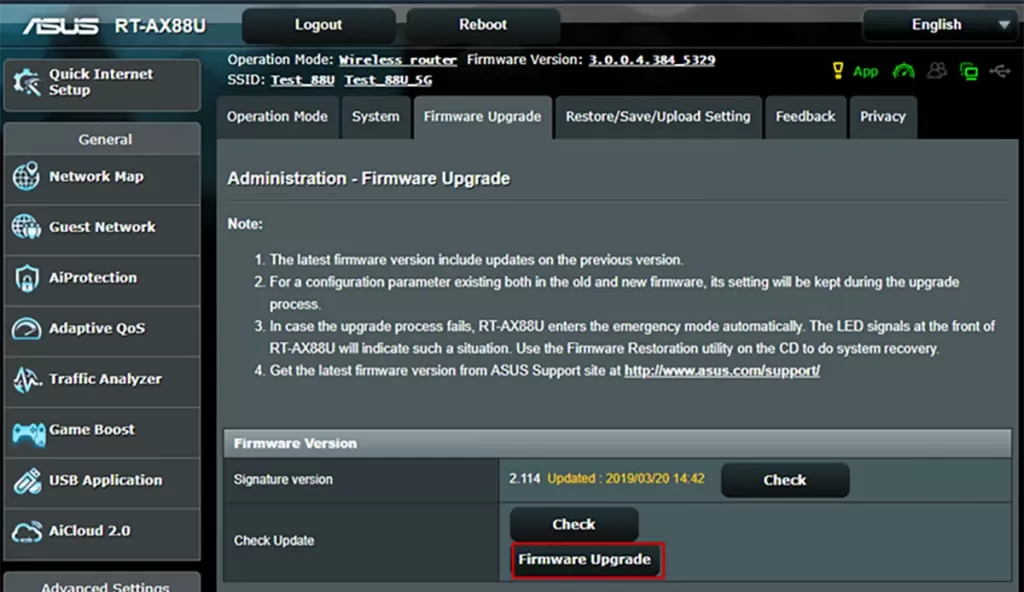
If your router downloads firmware automatically, you can skip this step. If manual download is required, identify the exact make and model of your device. Search the manufacturer's official website for the latest firmware version for your specific model and download the file to your computer. It is advisable to check for updates at least once a month.
Step 3: Install the Update
Return to the Firmware/Software Update section in the router's web interface. If you downloaded the file manually, there will be an option (often labeled "Upload" or "Browse") that allows you to transfer the downloaded file from your computer to the router.
If the router automatically downloaded the newest version, simply click the prompt to install it and begin the update process.
Step 4: Restart and Verify Connection
When the firmware update process begins, the router will restart automatically. This means all devices on the network will lose their internet connection for a few minutes. Plan the update accordingly to minimize disruption.
Once the router successfully restarts, the internet connection should be automatically restored, and your network is now running on the latest, most secure firmware.
4. Tips to Avoid Common Update Errors

While updating is usually simple, certain errors can occur. Follow these tips to ensure a smooth process:
- Use Official Sources Only: Always download the firmware manually from the manufacturer's official website, ensuring the file corresponds exactly to your router's model. Incorrect files will cause the update to fail.
- Download Old Firmware: Always download both the new and the previous firmware versions. If the update fails or introduces critical bugs, having the older file allows you to quickly reinstall the working previous version.
- Back Up the Configuration: Before starting, make a backup of your router's configuration. Although rare, updates can sometimes reset the router to factory settings. Having the backup of your IPs, DHCP, DNS, and open ports settings will save you significant time reconfiguring the network.
- Ensure Power Stability: Never interrupt power to the router during the update process. A power failure while flashing the firmware can permanently "brick" the device, making it unusable.
Conclusion
An updated firmware protects your data and systems against the latest cyber threats, ensures greater stability for your internet connection, and maintains compatibility with all your devices. Do not overlook this critical security step. Configure automatic updates if your router supports it, or set a recurring reminder to check your internet gateway's firmware status regularly.

Post a Comment for "Why It Is Critical to Update Your Router’s Firmware (and How to Do It Easily)"